Table of Contents
Matlab on Caviness
For use on Caviness, MATLAB projects should be developed using a Desktop installation of MATLAB and then copied to Caviness to be run in batch. Here an extended MATLAB example is considered involving one simple MATLAB function, and two MATLAB scripts to execute this function in a loop, and another to execute in parallel using the Parallel Computing Toolbox.
Details on how to run these two scripts in batch are given with the resulting output files. There is also a section with UNIX commands you can use to watch your jobs and gather timing and core count numbers. It is important to know how much memory will be needed and how many cores will be used to set your resource requirements. If you do not ask for enough memory your job will fail. If you do not ask for enough cores, the job will take longer.
Even though it easier to develop on a desktop, MATLAB can be run interactively on Caviness, however it is not recommended for scripts that are long and computationally intensive.
Two interactive jobs are demonstrated. One shows how to test the function by executing the function one time. A
second example shows an interactive session, which starts multiple MATLAB pool of workers to execute the function in a loop using the Parallel Computing toolbox command, parfor.
The Parallel Computing toolbox gives a faster time to completion, but more memory and CPU resources are consumed.
You can run MATLAB as a Desktop GUI application on Caviness, but again this is not recommended as the graphics are slow to display especially with a lower bandwidth network connection.
Many MATLAB research projects fall in the "high throughput computing" category. One run can be done on the desktop, but it is desired complete 100s or 1000s of independent runs. This greatly increases disk, memory and CPU requirements. Thus we have a final example that gives the recommended workflow to scale your job to multiple nodes. Compile the MATLAB code with single thread option and deploy the job as an grid engine array job.
Getting Started
There will be several examples covered in the following sections. To help make things easier to following it is suggested to make a new directory in your home directory ~/ or in your workgroup directory $WORKDIR . Then cd into the directory. In the new directory, you can add the maxEig.m and script.m files. These two files will be used in several of the examples.
[traine@login00 ~]$ mkdir matlab_example [traine@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example
As you go through the following example it is suggested that you also create a new directory, for each of them. It will help make it easier to follow and track output files of the different jobs that you will be running.
Now create the following file and put it in the ~/matlab_example directory
Matlab function
We will be using this sample function on the Caviness cluster in multiple demonstrations.
- maxEig.m
function maxe = maxEig(sd,dim) % maxEig maximum real eigenvalue of a normally distributed random matrix % Input parameters % sd - seed for random generator % dim - size of the square matrix % Output value % maxe - maximum real eigenvalue if (isdeployed) sd = str2num(sd) dim = str2num(dim) end rng(sd); ev = eig( randn(dim) ); maxe = max( ev(imag(ev)==0) ) end
The remainder of this page is based on using this MATLAB function to illustrate using MATLAB interactively and batch. The function will be executed interactively on multiple cores using multiple computational threads, and with 12 workers from a MATLAB pool. A MATLAB script with be run in batch to loop with multiple computational threads again using a MATLAB pool.
Finally it will be compiled and deployed using the MATLAB Compiler Runtime (MCR) environment.
isreal, but it is useless to select real values from a complex array, since it will return false for all the elements of a complex array. Thus we use the selecting reals by the property that their imaginary part is 0.0. This may be subject to round-off errors, both by selecting complex numbers with very small imaginary parts, or by not selecting some real eigenvalues where the imaginary part is non-zero from rounding.
maxe = max( ev(imag(ev)==0) ); fprintf('sd=%d counte=%d maxe=%.4f\n', sd, length(ev(imag(ev)==0)), maxe)
Matlab script
Now, write a MATLAB script file and put it in the ~/matlab_example directory. It should have a comment on the first line describing the purpose of the script and have the quit command on the last line. This script will call the maxEig function 200 times and report the average:
- script.m
% script to run maxEig function 200 times and print average. count = 200; dim = 5001; sumMaxe = 0; tic; for i=1:count; sumMaxe = sumMaxe + maxEig(i,dim); end; toc avgMaxEig = sumMaxe/count quit
This is a detailed script example, which calls the maxEig function. This example does no file I/O, all the I/O is to standard out. In MATLAB, assignments, not terminated by a semicolon, are displayed on the screen (standard out in batch).
-r script option, it will come back with a bash prompt when completed. If this is run from a batch job, then you can do other commands in your batch script after the MATLAB script completes.
Without the quit you will come back to the MATLAB prompt on completion for a interactive job. If this is the last line of a batch queue script, then the only difference will be the MATLAB prompt » at the very end of the output file. MATLAB treats the end of batch script file the same as exiting the window, which is the preferred way to exit the MATLAB GUI.
Copy the project folder
If you created the files on your desktop version of MATLAB, now copy the folder to your ~/matlab_example project directory on the cluster.
Use any file transfer client to copy your project directory.
Batch Job
You should have a copy of your MATLAB project directory on the cluster.
MATLAB has a new version twice a year. It is important to keep the version you use on your desktop the same as the one on the cluster. The command
vpkg_versions matlab
will show you the versions available on a cluster. Choose the one that matches the version on your desktop. We recommend you do not upgrade MATLAB in the middle of a project, unless there is a new feature or bug fix you need.
It is frequently advisable to keep your MATLAB project clean from non-MATLAB files such as the job script file and the script output file. But you may combine them, and even use the MATLAB editor to create the script file and look at the output file. If you create the file on a Windows desktop, take care to not transfer the files as binary. See Transferring Files to/from Caviness for details.
When you have one combined directory, do not put the cd command in the queue script; instead, change
to the project directory using cd on the command line, before submitting your job.
Create a job script file
You should create a job script file to submit a batch job. Start by modifying a batch job script template file (/opt/shared/templates/slurm/generic/serial.qs), for example, to submit a serial job using one core on a compute node,
In your newly copied serial.qs file, add the following lines at the end.
[traine@login00 matlab_example]$ cp /opt/shared/templates/slurm/generic/serial.qs matlab_first.qs
# Add vpkg_require commands after this line: vpkg_require matlab #Running the Matlab main_script matlab -nodisplay -singleCompThread -batch main_script
Note we did not specify a version of MATLAB with the VALET command, so we will get the default version (*) defined in VALET. This is okay for our examples, but in practice and reproducibility of your jobs, you should specify a MATLAB version. Now make a new file call main_script.m Add the below lines to the file.
display 'Hello World'
When this script runs it will display Hello World .
Submit batch job
Your shell must be in a workgroup environment
to submit any jobs.
Use the sbatch command to submit a batch job
and note the «JOBID» that is assigned to your job. For example, if your job script file name is matlab_first.qs, then to
submit the job you would type
sbatch matlab_first.qs
This is the message you get if you are not in a workgroup.
sbatch: error: Batch job submission failed: Invalid account or account/partition combination specified
It is true that a job script file is (usually) a bash script, but it must be executed with the sbatch command instead of the sh command. This way it is process by the job scheduler, Slurm, and the appropiate Slurm commands will allocate the requested resources and the job will be run on a compute node.
Wait for job to complete
You can check on the status of you job with the scontrol show job command.
For example, to list the information for job «JOBID», type
scontrol show job <<JOBID>>
For long running jobs, you could change your job script to notify you via an email message when the job is complete.
Post process job
All MATLAB output data files will be in the project directory, but the MATLAB standard output will be in
the current directory, from which you submitted the job. If you did not redefine Slurm output for your job, then you'll be looking for a file slurm-«JOBID».out.
Interactive job
Here are specific details for running MATLAB as an interactive job on a compute node. You should have a copy of your MATLAB project directory on the cluster and will be referred to a project_directory in the examples below.
Command-line
You should work on a compute node when in command-line MATLAB.
Your shell must be in a workgroup environment
to submit a single threaded interactive job using salloc.
[traine@login00 ~]$ workgroup -g it_css
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ salloc --partition=_workgroup_
salloc: Pending job allocation 7809686
salloc: job 7809686 queued and waiting for resources
salloc: job 7809686 has been allocated resources
salloc: Granted job allocation 7809686
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes r00n16 are ready for job
[traine@r00n16 ~]$ vpkg_require matlab
Adding package `matlab/r2018b` to your environment
[traine@r00n16 ~]$ cd matlab_example
[traine@r00n16 matlab_example]$ matlab -nodesktop -singleCompThread
MATLAB is selecting SOFTWARE OPENGL rendering.
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2018b (9.5.0.944444) 64-bit (glnxa64)
August 28, 2018
To get started, type doc.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
>>
This will start a interactive command-line session in your terminal window. When done type the quit or exit to terminated the MATLAB session and then exit to terminated the salloc session. Again note, a specific version of MATLAB was not specified, so at the time of writing this wiki page the default version defined in VALET was version 2018b.
MATLAB is selecting SOFTWARE OPENGL rendering.
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2018b (9.5.0.944444) 64-bit (glnxa64)
August 28, 2018
To get started, type doc.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
>>quit
[traine@r00n16 matlab_example]$ exit
exit
salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 7809686
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$
Desktop
You should be on a compute node before you start MATLAB. To start a MATLAB desktop (GUI mode) on a cluster, you must be running an X11 server and you must have connected to the cluster with ssh using X11 tunneling.
You must be in a workgroup environment to submit a job using salloc.
[traine@login00 ~]$ workgroup -g it_css [(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ salloc --x11 -N1 -n1 --partition=_workgroup_ salloc: Pending job allocation 7790913 salloc: job 7790913 queued and waiting for resources salloc: job 7790913 has been allocated resources salloc: Granted job allocation 7790913 salloc: Waiting for resource configuration salloc: Nodes r00n10 are ready for job [traine@r00n10 ~]$ vpkg_require matlab Adding package `matlab/r2018b` to your environment [traine@r00n10 ~]$ matlab MATLAB is selecting SOFTWARE OPENGL rendering.
This will start an interactive MATLAB desktop GUI mode session on your desktop in an X11 window using your workgroup resources.
When done type the quit or exit in the command window or just close the window. When back at the terminal bash prompt, type exit to terminate the salloc interactive session and return to the login (head) node.
See tips on starting MATLAB in an interactive session without the desktop, including executing a script.
For more information, review the instructions for setting up X11 connections with an SSH connection for Windows, Mac, and Linux OS.
For more information on GUI Applications on Caviness, visit Launching GUI Applications (X11 Forwarding).
Compiling with Matlab
We show the three most common ways to work with compilers when using MATLAB.
- Compiling your Matlab code to run in the MCR (MATLAB Compiler Runtime)
- Compiling your C or Fortran program to call MATLAB engine.
- Compiling your own function in C or Fortran to be used in a MATLAB session.
Warning: You are using gcc version '4.9.3'. The version currently supported with MEX is '4.7.x'. For a list of currently supported compilers see: http://www.mathworks.com/support/compilers/current_release.
But the compilation completes successfully.
Compiling your Matlab code
There is an example MCR project in the /opt/shared/templates/ directory for you to copy and try. Copy on the head node and use salloc to compile with MATLAB on the devel partition (.i.e max request time on the devel partition is 2 hours and 4 cores). Once your program is compiled, you can run it interactively or batch, without needing a MATLAB license.
Copy dev-projects template
On the head node, copy the example project into your current directory using the following commands
[traine@login00 ~]$ workgroup -g it_css [(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cp -r /opt/shared/templates/dev-projects/Projects/MCR . [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cd MCR
Compile with make
Now compile on the compute node by using
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR]$ salloc --partition=devel salloc: Granted job allocation 7861739 salloc: Waiting for resource configuration salloc: Nodes r00n56 are ready for job [triane@r00n56 MCR]$
salloc. The prompt ([(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR]$) displays the workgroup (e.g. it_css) in this example. Also in this example specifying no other options, our job will be assigned to the devel partition for 30 minutes, 1 core and 1GB memory.
Check and edit the VALET command in the Makefile to load the appropriate version of the MATLAB Compile Runtime (mcr) package. In this example, we edited the Makefile to load mcr/r2019b:nojvm, so the resulting output from the make command produces:
[traine@r00n56 MCR]$ make
Adding package `mcr/2019b:nojvm` to your environment
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/2179/documents/matlab_example/MCR'
mcc -o maxEig -I ./common -R ""-nojvm,-nodesktop,-singleCompThread"" -v -m maxEig.m
Compiler version: 7.1 (R2019b)
Dependency analysis by REQUIREMENTS.
Parsing file "/home/1201/documents/matlab_example/MCR/maxEig.m"
(referenced from command line).
Generating file "/home/1201/documents/matlab_example/MCR/readme.txt".
Generating file "run_maxEig.sh".
make[1]: Leaving directory `/home/1201/documents/matlab_example/MCR'
Take note of the package added, and the files that are generated. You can remove these files, as they are not needed.
Remember the VALET command used to load the appropriate version of the mcr package for compiling will also need to be the same command (same version of mcr) used to run your compiled code either interactively or batch.
Test interactively
To test interactively on the same compute node.
[traine@r00n56 MCR]$ vpkg_require mcr/r2019b:nojvm Adding package `mcr/2019b:nojvm` to your environment [traine@r00n56 MCR]$ time ./maxEig 20.8 maxe = 510.8787 real 6m58.608s user 6m38.486s sys 0m6.114s
back to the head node
When done, type exit to terminate the salloc interactive session and return to the login (head) node.
[traine@r00n56 MCR]$ exit exit salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 7861739 [(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR]$
Test batch
Copy array job example
On the head node, copy the MCR array example project and the matlab-mcr.qs template job script file into your current directory using the following commands
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cp -r /opt/shared/templates/dev-projects/Projects/MCR MCR_array
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd MCR_array
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array]$ cp /opt/shared/templates/slurm/applications/matlab-mcr.qs .
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array]$ make
Adding package `mcr/2019b` to your environment
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/2179/documents/matlab_example/MCR_array'
mcc -o maxEig -I ./common -R ""-nojvm,-nodesktop,-singleCompThread"" -v -m maxEig.m
Compiler version: 7.1 (R2019b)
Dependency analysis by REQUIREMENTS.
Parsing file "/home/2179/documents/matlab_example/MCR_array/maxEig.m"
(referenced from command line).
Generating file "/home/2179/documents/matlab_example/MCR_array/readme.txt".
Generating file "run_maxEig.sh".
make[1]: Leaving directory `/home/2179/documents/matlab_example/MCR_array'
The following lines will need to be changed or added to the matlab-mcr.qs file. Please read through all the comments, but we have provided the line number preceding the code where the alteration is needed for this example. Keep in mind for this example we are compiling with -single-comp-thread so we would not need to alternate to request additions cores (--ntasks).
...
36 #SBATCH --mem=3G
...
54 #SBATCH --job-name=matlab_mcr_arrray
...
65 #SBATCH --partition=_workgroup_
...
92 #SBATCH --output arrayJob-%A-%3a.out
...
117 # Setting the job array options
118 #SBATCH --array=1-100:1
...
157 # Load a specific Matlab MCR package into the runtime environment:
158 #
159 vpkg_require mcr/r2019b:nojvm
160
161 #
162 # Do standard MCR environment setup:
163 #
164 . /opt/shared/slurm/templates/libexec/matlab-mcr.sh
165
166 #
167 # Execute your MCR program(s) here; prefix with UD_EXEC to
168 # ensure the job can/will respond to preemption/termination
169 # signals by calling your UD_JOB_EXIT_FN.
170 #
171 # Duplicate all three commands for each MCR program you run
172 # in sequence below.
173 #
174 #UD_EXEC my_mcr_program arg1 arg2
175 #mcr_rc=$?
176 #if [ $mcr_rc -ne 0 ]; then exit $mcr_rc; fi
177
178 echo "Job Running on Host: $HOSTNAME"
179
180 start=$(date "+%s")
181 echo "Job Start: ${start}"
182
183 #Using the Slurm task ID as an argurment lambda to MaxEig
184 let lambda=$SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID
185
186 #Lines Added for MCR_array example
187 UD_EXEC ${HOME}/documents/matlab_example/MCR_array/maxEig $lambda
188 mcr_rc=$?
189 if [ $mcr_rc -ne 0 ]; then exit $mcr_rc; fi
190
191 finish=$(date "+%s")
192 echo "Job Finish: ${finish}"
193
194 runtime=$(($finish-$start))
195
196 echo "Total Runtime: ${runtime}"
Example sbatch submission
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR]$ sbatch matlab-mcr.qs Submitted batch job 9803575 [(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR]$ date Fri Oct 30 08:57:58 EDT 2020 [(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR]$ date Fri Oct 30 08:58:19 EDT 2020 [(it_css:traine)@traine MCR]$ ls -l MCR_array-9803575* | wc -l 100
There are 100 output files with the names MCR_array-9803575-001.out to MCR_array-9803575-100.out
For example, file 50 which is MCR_array-9803575-050.out looks like this:
Adding package `mcr/2019b` to your environment -- Matlab MCR environment setup complete (on r00n13): -- MCR_ROOT = /opt/shared/matlab/r2019b -- MCR_CACHE_ROOT = /tmp/job_9803625 Job Running on Host: r00n13.localdomain.hpc.udel.edu Job Start: 1604062673 maxe = 525.9320 Job Finish: 1604062704 Total Runtime: 31
more examples Under construction: Stay tuned
Compiling your code to use MATLAB engine
Here is an simple example function called fengdemo.F coded in Fortran, you can copy and use as a starting point.
On the head node and in your workgroup shell:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ mkdir matlab_compile
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cd matlab_compile
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_compile]$ vpkg_require matlab/r2019a gcc/9.1
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_compile]$ cp $MATLABROOT/extern/examples/eng_mat/fengdemo.F .
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_compile]$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$MATLABROOT/bin/glnxa64:$MATLABROOT/sys/os/glnx64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_compile]$ mex -client engine fengdemo.F
Warning: MATLAB FORTRAN MEX Files are now defaulting to -largeArrayDims and 8 byte integers.
If you are building a FORTRAN S-Function, please recompile using the -compatibleArrayDims flag.
You can find more about adapting code to use 64-bit array dimensions at:
https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_external/upgrading-mex-files-to-use-64-bit-api.html.
Building with 'gfortran'.
MEX completed successfully.
[(it_css:triane)@login00 matlab_compile]
To run this program it will require running an interactive session on a compute node with X11 forwarding enabled. Here is an example for user traine in workgroup it_css:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_compile]$ salloc --x11 -N1 -n1 --partition=_workgroup_ salloc: Granted job allocation 7915683 salloc: Waiting for resource configuration salloc: Nodes r03g07 are ready for job [traine@r03g07 matlab_compile]$ vpkg_require matlab/r2019a gcc/9.1 Adding package `matlab/r2019a` to your environment Adding package `gcc/9.1.0` to your environment [traine@r03g07 matlab_compile]$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$MATLABROOT/bin/glnxa64:$MATLABROOT/sys/os/glnx64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH [traine@r03g07 matlab_compile]$ ./fengdemo
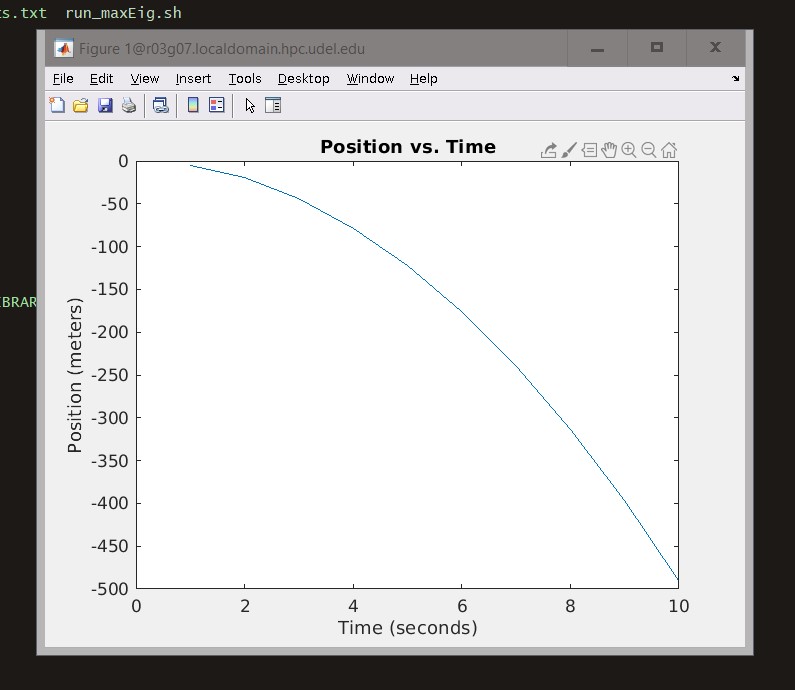
Shortly after starting to run the the program, ./fengdemo, a Matlab window will open and display a chart below
After the Matlab window is opened, you will see a prompt in the terminal to "Exit" or "Continue". Typing 1and pressing the Enter key will return a table which is shown below.
After the table is returned, close the MATLAB window with the Chart. Then use the exit command to release the computer node.
Type 0 <return> to Exit Type 1 <return> to continue 1 MATLAB computed the following distances: time(s) distance(m) 1.00 -4.90 2.00 -19.6 3.00 -44.1 4.00 -78.4 5.00 -123. 6.00 -176. 7.00 -240. 8.00 -314. 9.00 -397. 10.0 -490. [traine@r03g07 matlab_compile]$ exit salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 7915683 [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_compile]$
Compiling your own MATLAB function
There is an simple example function timestwo.c, coded in c, you can copy and use as a starting point.
On the head node and in a workgroup shell:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ mkdir matlab_function [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cd matlab_function [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_function]$ vpkg_require matlab/r2019a gcc/9.1 Adding package `matlab/r2019a` to your environment Adding package `gcc/9.1.0` to your environment [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_function]$ cp $MATLABROOT/extern/examples/refbook/timestwo.c . [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_function]$ mex timestwo.c Building with 'gcc'. Warning: You are using gcc version '9.1.0'. The version of gcc is not supported. The version currently supported with MEX is '6.3.x'. For a list of currently supported compilers see: https://www.mathworks.com/support/compilers/current_release. MEX completed successfully. [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_function]$
To start MATLAB on a compute node to test this new function:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_function]$ salloc --partition=devel
salloc: Pending job allocation 7916296
salloc: job 7916296 queued and waiting for resources
salloc: job 7916296 has been allocated resources
salloc: Granted job allocation 7916296
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes r00n56 are ready for job
[traine@r00n56 matlab_function]$ vpkg_require matlab/r2019a gcc/9.1
[traine@r00n56 matlab_function]$ matlab -nodesktop
MATLAB is selecting SOFTWARE OPENGL rendering.
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2019 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2019a (9.6.0.1072779) 64-bit (glnxa64)
March 8, 2019
To get started, type doc.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
>>
Now test the function by typing timestwo(4). The results are shown below. Afterwards type quit to exit Matlab and then type exit to release the compute node.
>> timestwo(4)
ans =
8
>> quit
[traine@r00n56 matlab_function]$ exit
exit
salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 7916296
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_function]$
Batch job serial example
Second, write a shell script file to set the MATLAB environment and start MATLAB running your script file. The following script file will set the MATLAB environment and run the command in the script.m file:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ mkdir matlab_slurm [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cd matlab_slurm [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ cp /opt/shared/templates/slurm/generic/serial.qs batch.qs [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ vim batch.qs
- batch.qs
... 40 #SBATCH --job-name=script.m ... 50 #SBATCH --partition=_workgroup_ ... 67 #SBATCH --time=0-03:00:00 ... 76 #SBATCH --output %x-%j.out 77 #SBATCH --error %x-%j.out ... 86 #SBATCH --mail-user='traine@udel.edu' 87 #SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL,TIME_LIMIT_90 ... 137 # 138 # [EDIT] Add your script statements hereafter, or execute a script or program 139 # using the srun command. 140 # 141 #srun date 142 #Loading MATLAB 143 vpkg_require matlab/r2018b 144 #Running the matlab script 145 matlab -nodisplay -nojvm -batch script
Make sure you change the --mail-user from traine@udel.edu to your preferred email address. The -nodisplay indicates no X11 graphics, which implies -nosplash -nodesktop. The -nojvm indicates no Java. (Java is needed for some functions, e.g., print graphics, but should be excluded for most computational jobs.)
The -batch is followed by a Matlab command, enclosed in quotes when there is are spaces in the command.
script will execute the lines in the script.m file. For some errors Matlab will display the error message and wait for a response – clearly not appropriate for a batch job. Consider replacing script with
the compound command
"try; script; catch ERR; disp(getReport(ERR,'extended')); quit; end"
The purpose of the try/catch block is to catch the first error in the script, and display a report. With the extended option the report will include a stack trace at the point of the error.
- Do not include the
-nojvmon the matlab command. - Do set paper dimensions and print each figure to a file.
The text output will be included in the standard Slurm output file, but not any graphics. All figures must be exported using the print command. Normally the print command will print on an 8 1/2 by 11 inch page with margins that are for a printed page of paper. The size and margins will not work if you plan to include the figure in a paper or a web page.
We suggest setting the current figure's PaperUnits, PaperSize and PaperPosition. Matlab provides a handle to the current figure (gcf). For example, the commands
set(gcf,'PaperUnits','inches','PaperSize',[4,3],'PaperPosition',[0 0 4 3]); print('-dpng','-r100','maxe.png');
will set the current figure to be 4 x 3 inches with no margins, and then print the figure as a 400x300 resolution png file.
Submit job
Third, from the directory with script.m, maxEig.m and batch.qs, submit the batch job with the command:
sbatch batch.qs
Wait for completion
Finally, wait for the mail notification, which will be sent to traine@udel.edu unless you changed it to your preferred email address. When the job is done, the output from the MATLAB command will be in a file with the pattern script.m-«JOBID».out, where JOBID is the number assigned to your job.
After waiting for about 2 or 3 hours, a message was received from SLURM Administrator. The email will have a title like the one shown below and there will be no content in the body.
SLURM Job_id=7937771 Name=script.m Ended, Run time 02:47:11, COMPLETED, ExitCode 0
Gather results
The results for Job 7937771 are in the file
- script.m-7937771.out
Fri Apr 10 16:36:38 EDT 2020 Adding package `matlab/r2018b` to your environment < M A T L A B (R) > Copyright 1984-2018 The MathWorks, Inc. R2018b (9.5.0.944444) 64-bit (glnxa64) August 28, 2018 For online documentation, see https://www.mathworks.com/support For product information, visit www.mathworks.com. maxe = 70.0220 maxe = 71.7546 maxe = 70.8331 maxe = 70.5714 maxe = 69.4923 maxe = 67.7814 maxe = 70.5037 maxe = 68.3293 maxe = 69.5694 ... //Skipping 953 similar displays of variable maxe// maxe = 67.4221 Elapsed time is 10023.165546 seconds. avgMaxEig = 69.5131
Timings and core count
Consider a batch job run with these Slurm options:
#SBATCH --ntasks=5
#SBATCH --mem=1G
#SBATCH --job-name=script_opt.m
The sbatch command will assign a JOBID, and once it starts running, the squeue command will show the node you are running on and we can use it to set n=r01n17 and refer to it as $n for our series of next commands. After about 10 minutes of running:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ n=r01n17 [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ echo $n r01n17 [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ ssh $n ps -eo pid,ruser,pcpu,pmem,thcount,stime,time,command | egrep '(COMMAND|matlab)' PID RUSER %CPU %MEM THCNT STIME TIME COMMAND 10853 traine 100 0.6 12 13:56 00:19:53 /opt/shared/matlab/r2018b/bin/glnxa64/MATLAB -nodisplay -batch script -nojvm
This ps command will give the percent CPU, which is = >100% for multi-core jobs, the percent memory, the thread count, which is > 5, the start time, the time of executions, and finally the full command used to the start the job.
Given the reported PID 10853, you can drill down and see which of the 10 threads are consuming CPU time:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ ssh $n ps -eLf | egrep '(PID|10853)' | grep -v ' 0 ' UID PID PPID LWP C NLWP STIME TTY TIME CMD traine 10853 10778 10906 99 12 13:56 ? 00:27:05 /opt/shared/matlab/r2018b/bin/glnxa64/MATLAB -nodisplay -batch script -nojvm
While the batch job was running on node r01n17, the top command was run to sample the resources being used by MATLAB
every second -b -n 1 and can only be used on computing nodes you have jobs running. The -H option was used to display each individual thread, rather than a summary of all threads in a process.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ ssh $n top -H -b -n 1 | egrep '(COMMAND|MATLAB)' | grep -v 'S 0' PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND 10906 traine 20 0 2450792 859664 105120 R 99.9 0.7 28:47.25 MATLAB
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ qhost -h $n HOSTNAME ARCH NCPU NSOC NCOR NTHR NLOAD MEMTOT MEMUSE SWAPTO SWAPUS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- r01n17 E5-2695v4 36 2 36 36 0.03 124.0G 1024.0M 0.0 0.0
After the job is done you can use sacct to get a recap of resources used:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ sacct -N r01n17 -j 7935464 -o jobName,jobID,Nodelist,maxVMSize,MaxRSS,CPUTime,Start,End,Elapsed,State
JobName JobID NodeList MaxVMSize MaxRSS CPUTime Start End Elapsed State
---------- ------------ --------------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------------- ------------------- ---------- ----------
script_op+ 7935464 r01n17 14:06:35 2020-04-10T13:56:18 2020-04-10T16:45:37 02:49:19 COMPLETED
batch 7935464.bat+ r01n17 209328K 755008K 14:06:35 2020-04-10T13:56:18 2020-04-10T16:45:37 02:49:19 COMPLETED
extern 7935464.ext+ r01n17 182456K 20K 14:06:40 2020-04-10T13:56:18 2020-04-10T16:45:38 02:49:20 COMPLETED
date 7935464.0 r01n17 277996K 488K 00:00:05 2020-04-10T13:56:21 2020-04-10T13:56:22 00:00:01 COMPLETED
Batch job parallel example
The MATLAB Parallel Computing toolbox uses JVM to manage the workers and communicate while you are running. You
need to setup the MATLAB pools in your script.
Matlab parallel script
Here is the slightly modified MATLAB script.
Add the necessary commands to configure your parcluster and parpool, and change for ⇒ parfor.
- pscript.m
% script to run maxEig function 200 times %% Configure parpool myCluster = parcluster('local'); myCluster.NumWorkers = str2double(getenv('SLURM_NTASKS')); myCluster.JobStorageLocation = getenv('TMPDIR'); myPool = parpool(myCluster, myCluster.NumWorkers); count = 200; dim = 5001; sumMaxe = 0; tic parfor i=1:count; sumMaxe = sumMaxe + maxEig(i,dim); end toc avgMaxEig = sumMaxe/count delete(myPool); exit
Slurm parallel script
Remove the option -nojvm, because JVM is needed for the Parallel Computing toolbox commands.
Copy the template matlab.qs script and name it pbatch.qs by typing
cp /opt/shared/templates/slurm/applications/matlab.qs ./pbatch.qs
Make the following changes to the code
- pbatch.qs
... 19 #SBATCH --ntasks=20 ... 37 #SBATCH --mem=60G ... 54 #SBATCH --job-name=matlab-pscript ... 65 #SBATCH --partition=_workgroup_ ... 75 #SBATCH --time=0-01:00:00 ... 82 #SBATCH --time-min=0-00:30:00 ... 90 #SBATCH --output=%x-%j.out 91 #SBATCH --error=%x-%j.out ... 155 vpkg_require matlab/r2019b ... 170 UD_EXEC matlab -nodisplay -batch pscript
Timing results
Reported usage for same job run using the parallel toolbox.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_slurm]$ sacct -j 7994763,7997035 -o jobName,jobID,Nodelist,maxVMSize,MaxRSS,CPUTime,Start,End,Elapsed,State
JobName JobID NodeList MaxVMSize MaxRSS CPUTime Start End Elapsed State
---------- ------------ --------------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------------- ------------------- ---------- ----------
script.m 7994763 r01n49 4-05:01:12 2020-04-15T11:16:06 2020-04-15T14:04:28 02:48:22 COMPLETED
batch 7994763.bat+ r01n49 209328K 804888K 4-05:01:12 2020-04-15T11:16:06 2020-04-15T14:04:28 02:48:22 COMPLETED
extern 7994763.ext+ r01n49 107904K 20K 4-05:01:12 2020-04-15T11:16:06 2020-04-15T14:04:28 02:48:22 COMPLETED
pscript 7997035 r03n38 09:33:20 2020-04-15T15:56:42 2020-04-15T16:11:02 00:14:20 COMPLETED
batch 7997035.bat+ r03n38 209460K 14462792K 09:33:20 2020-04-15T15:56:42 2020-04-15T16:11:02 00:14:20 COMPLETED
extern 7997035.ext+ r03n38 107952K 0 09:33:20 2020-04-15T15:56:42 2020-04-15T16:11:02 00:14:20 COMPLETED
Compare script vs pscript
| Job | Elapsed Time | CPUTime | Max RSS |
|---|---|---|---|
| script.m | 02:48:22 | 4-05:01:12 | 804888K |
| pscript | 00:19:35 | 09:33:20 | 14462792K |
The job script used more CPU resources with the multiple computational threads, while pscript user more memory resources with 20 single-threaded worker.
Interactive job example
The basic steps to running a MATLAB interactively on a compute node that will dedicate specific resources to your job.
Scheduling interactive job
Create a directory and add maxEig.m and script.m to it.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ mkdir matlab_interact [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cp maxEig.m script.m matlab_interact/ [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cd matlab_interact [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_interact]$ ls maxEig.m script.m
Start an interactive session on a compute node with the salloc command. You will also want to include the options for the number of cores ntasks and –partition=_workgroup_.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_interact]$ salloc --partition=_workgroup_ --ntasks=20 salloc: Pending job allocation 7985695 salloc: job 7985695 queued and waiting for resources salloc: job 7985695 has been allocated resources salloc: Granted job allocation 7985695 salloc: Waiting for resource configuration salloc: Nodes r01n10 are ready for job [traine@r01n10 matlab_interact]$
Starting a command mode matlab session
[traine@r01n10 matlab_interact]$ vpkg_require matlab/r2019b Adding package `matlab/r2019b` to your environment [traine@r01n10 matlab_interact]$
[traine@r01n10 matlab_interact]$ matlab -nodesktop -nosplash
MATLAB is selecting SOFTWARE OPENGL rendering.
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2019 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2019b (9.7.0.1190202) 64-bit (glnxa64)
August 21, 2019
To get started, type doc.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
>>
Using help as the first command
>> help maxEig
maxEig Maximum Eigenvalue of a random matrix
Input parameters
sd - seed for uniform random generator
dim - size of the square matrix (should be odd)
Output value
maxe - maximum real eigvalue
Calling function once
Use the tic and toc commands to report the elapsed time to generate the random matrix, find all eigenvalues and report the maximum real eigenvalue.
>> tic; maxEig(1,5001); toc maxe = 70.0220 Elapsed time is 54.781289 seconds.
Finishing up
>> exit [traine@r01n10 matlab_interact]$ exit exit salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 7985695 [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_interact]$
Interactive parallel toolbox example
This example is based on the matlab_interact directory that was created in the Interactive job example demo shown above.
When you using the parallel toolbox, you should logon to a compute node using a workgroup partition and the number of tasks and memory required:
[(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_interact]$ salloc --partition=_workgroup_ --ntasks=20 --mem=40G salloc: Pending job allocation 7993736 salloc: job 7993736 queued and waiting for resources salloc: job 7993736 has been allocated resources salloc: Granted job allocation 7985815 salloc: Waiting for resource configuration salloc: Nodes r00g01 are ready for job [traine@r00g01 matlab_interact]$ vpkg_require matlab/r2019b [traine@r00g01 matlab_interact]$ matlab -nodesktop -nosplash
This will effectively reserve 20 cpus and 40G of memory for your interactive job. The default number of parallel workers when using the parallel toolbox is 12 but you can define the number workers based on the number of tasks requested.
Here we request 20 workers with the parpool function, and then use parfor to send a different seed to each worker. The output is from the workers, as they complete, but the order is not deterministic.
It took about 100 seconds for all 20 workers to produce a result, however since there are 20 workers working in parallel the elapsed time to complete 200 results is about 918 seconds.
MATLAB is selecting SOFTWARE OPENGL rendering.
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2019 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2019b (9.7.0.1190202) 64-bit (glnxa64)
August 21, 2019
To get started, type doc.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
>> myCluster = parcluster('local');
>> myCluster.NumWorkers = str2double(getenv('SLURM_NTASKS'));
>> myCluster.JobStorageLocation = getenv('TMPDIR');
>> myPool = parpool(myCluster, myCluster.NumWorkers);
Starting parallel pool (parpool) using the 'local' profile ...
Connected to the parallel pool (number of workers: 20).
>> tic; parfor sd = 1:200; maxEig(sd,5001); end; toc
maxe =
67.1320
maxe =
70.8721
maxe =
71.3507
... skipped lines ...
maxe =
70.7506
maxe =
70.2656
maxe =
71.4253
Elapsed time is 918.822702 seconds.
Once the job is completed, delete your pool and exit MATLAB, and release the interactive compute node by typing exit.
>> delete(myPool); Parallel pool using the 'local' profile is shutting down. >> exit [traine@r00g01 matlab_interact]$ exit exit salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 7993736 [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_interact]$
MCR array job example
Most Matlab functions can be compiled using the Matlab Compiler (mcc) and then deployed to run on the compute nodes in the MATLAB Compiler Runtime (MCR). The MCR is a prerequisite for deployment, and is installed on all the compute nodes. You must use VALET to set up the libraries you will need to run your function from the command line. You should NOT to use the shell (.sh file) that the Matlab compiler creates.
There are two ways to run compiled MATLAB jobs in a shared environment, such as Caviness.
- Compile to produce an executable that uses a single computational thread specifying the MATLAB option
-singleCompThread - Submit the job to use the nodes exclusively specifying the Slurm option
–exclusive
You can run more jobs on each node when they are compiled using just one core (Single Computational Thread). This will give you higher throughput for an array job, but not higher performance.
Example compiler commands
Make a new directory MCR_array_II directory and then copy maxEig function from the matlab_example directory to the new MCR_array_II directory.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ mkdir MCR_array_II [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cp maxEig.m MCR_array_II/ [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ cd MCR_array_II
The maxEig function has a conditional statement to make it work when deployed.
if (isdeployed)
sd = str2num(sd)
dim = str2num(dim)
end
All arguments of the function are taken as tokens on the shell command used to execute the script, and they are all strings. You must convert numbers from strings to numbers. You can use the same variable names so that the rest of the script will behave the same when deployed or executed directly in Matlab.
You can convert this function into a single computational executable by using the Matlab compiler mcc. To do this, create a file compile.sh and add the below line to the file.
prog=maxEig
opt='-nojvm,-nodisplay,-singleCompThread'
version='r2019a'
vpkg_require matlab/$version
mcc -R "$opt" -mv $prog.m
[ -d ${WORKDIR}/${USER}/sw/bin ] && mv $prog ${WORKDIR}/${USER}/sw/bin
maxEig. You will need to know these if you want to use the executable in a shell script. You can source this file when you want to rebuild maxEig
mcc -help: The string following the -R flag are the Matlab
options you want to use at run time. The -m option tell mcc to build a standalone application to be deployed
using MCR. The -v option is for verbose mode.
lustre file system. That is why the executable $prog is moved to the special directory, which is added to your path when a new workgroup shell is started or when a queue script is submitted.
[ -d $WORKDIR/sw/bin ] && mv $prog $WORKDIR/sw/bin
Compiling commands
Make the directory where the MaxEig function will be placed when the function is compiled.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array_II]$ mkdir -p ${WORKDIR}/${USER}/sw/bin
Now request a interactive compute node and run the compile.sh script.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array_II]$ salloc --partition=devel
salloc: Granted job allocation 9804138
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes r00n56 are ready for job
[traine@r00n56 MCR_array_II]$ ls
compile.sh maxEig.m
[traine@r00n56 MCR_array_II]$ . compile.sh
Adding package `matlab/r2019b` to your environment
Compiler version: 7.1 (R2019b)
Dependency analysis by REQUIREMENTS.
Parsing file "/home/1201/matlab_example/MCR_array_II/maxEig.m"
(referenced from command line).
Generating file "/home/1201/matlab_example/MCR_array_II/readme.txt".
Generating file "run_maxEig.sh".
[traine@r00n56 MCR_array_II]$ ls
compile.sh maxEig.m mccExcludedFiles.log readme.txt requiredMCRProducts.txt run_maxEig.sh
[traine@r00n56 MCR_array_II]$ exit
exit
salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 9804138
[(it_css:traine)@login01 MCR_array_II]$
Example queue script file
The mcc command will generate a .sh file should not be used. This run script does not use VALET and does not have the appropriate Slurm commands. Instead, you should copy the Slurm template in the file
/opt/shared/templates/slurm/applications/matlab-mcr.qs by using the following command
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array_II]$ cp /opt/shared/templates/slurm/applications/matlab-mcr.qs .
and make the appropriate changes below changes.
...
20 #SBATCH --ntasks=2
...
29 #SBATCH --mem=3G
...
47 #SBATCH --job-name=maxEig
...
58 #SBATCH --partition=_workgroup_
...
85 #SBATCH --output %x-%A-%3a.out
...
102 # Setting the job array options
103 #SBATCH --array=1-200:1
...
148 # Load a specific Matlab MCR package into the runtime environment:
149 #
150 vpkg_require mcr/r2019b:nojvm
151 export MCR_CACHE_ROOT="$TMPDIR"
152
153 #
154 # Do standard MCR environment setup:
155 #
156 . /opt/shared/slurm/templates/libexec/matlab-mcr.sh
157
158 #
159 date "+Start %s"
160 echo "Host ${HOSTNAME}"
161
162
163 #Getting the ask ID that will be passed as a argument
164 let seed=$SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID
165 let dim=5001
166
167 # Execute your MCR program(s) here; prefix with UD_EXEC to
168 # ensure the job can/will respond to preemption/termination
169 # signals by calling your UD_JOB_EXIT_FN.
170 #
171 # Duplicate all three commands for each MCR program you run
172 # in sequence below.
173 #
174 #UD_EXEC my_mcr_program arg1 arg2
175 #mcr_rc=$?
176 #if [ $mcr_rc -ne 0 ]; then exit $mcr_rc; fi
177 UD_EXEC ${WORKDIR}/${USER}/sw/bin/maxEig $seed $dim
178 mcr_rc=$?
179 if [ $mcr_rc -ne 0 ]; then exit $mcr_rc; fi
180
181 date "+Finish %s"
182
The two date commands record the start and finish time in seconds for each task. These are then used to compute the total runtime. The echoed host name can be used to calculate the overlapping use of the computer nodes. Since maxEig was compiled as a single threaded job the elapse time will be very close to the wall clock time and CPU time. We do not send email notification since it would generated 200 email messages, one for each task.
Running Compiled Matlab Example In Workgroup And Analyzing Output Results
To test the example compiled Matlab job on the it_css owner queues, we first compiled the code with mcc and
then submited with sbatch.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array_II]$ sbatch matlab-mcr.qs Submitted batch job 9805558
The assigned job number ID assigned is 9805282. After a few minutes 200 files were created in the current directory.
maxEig-9805558-001.out ... maxEig-9805558-200.out
They each had the output of one task. For example for taskid 125:
Adding package `mcr/2019b:nojvm` to your environment
-- OpenMP job setup complete:
-- OMP_THREAD_LIMIT = 2
-- OMP_PROC_BIND = true
-- OMP_PLACES = cores
-- MP_BLIST = 32,33
-- Matlab MCR environment setup complete (on r00n10):
-- MCR_ROOT = /opt/shared/matlab/r2019b
-- MCR_CACHE_ROOT = /tmp/job_9805684
Start 1604084921
Host r00n10.localdomain.hpc.udel.edu
sd =
125
dim =
5001
maxe =
70.4891
Finish 1604085004
Now we will use wikigather.pl to gather all the information from this files and return the avgMaxEig value.
User the link to copy the code perl code, and them create new file in your current directory with that same name wikigather.pl and add the copied code into that file.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array_II]$ perl wikigather.pl avgMaxEig = 69.5131125
The script will all create three new .data files and one new .txt file. We are really on interested in the results8012246.data and the wikimaxEig.txt files. Examples of them are shown below.
sd dim maxe 1 5001 70.0220 2 5001 71.7546 3 5001 70.8331 4 5001 70.5714 5 5001 69.4923 .... 195 5001 68.7440 196 5001 71.5652 197 5001 69.8530 198 5001 70.1213 199 5001 70.7535 200 5001 67.4221
These are the same results we got from both the matlab loop and the parallel toolbox, but they where computed in just about 8.5 minutes. To see this we gather the start/finish times in seconds and the host name.
wiki9805558.txt Output:
SGE array job started Fri 30 Oct 2020 03:04:16 PM EDT
Used a total of 16585 CPU seconds over 525 seconds of elapsed time on 2 nodes
| Node | Real Clock Time | Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Count | Min | Max | Average | User/Real |
| r00n10.localdomain.hpc.udel.edu | 108 | 82.00 | 85.00 | 83.32 | 1.00000 |
| r00n47.localdomain.hpc.udel.edu | 92 | 58.00 | 84.00 | 82.46 | 1.00000 |
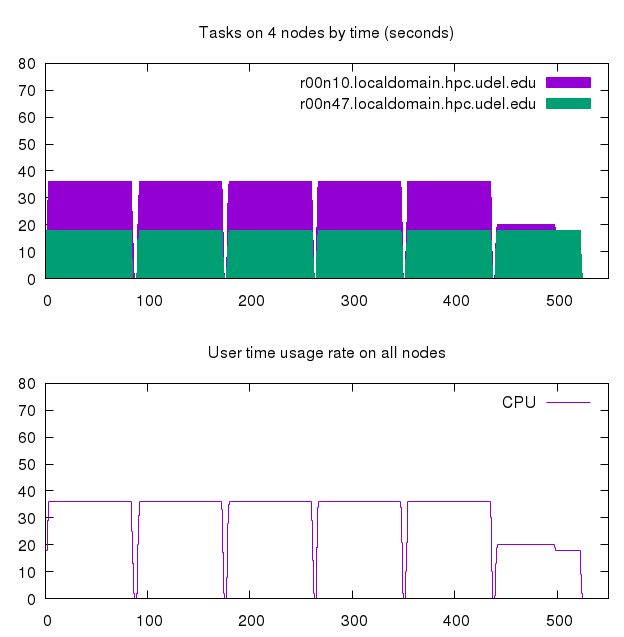
Using gnuplot we get a time chart of usage on the 2 nodes and total CPU usage.
Create a file and add the following code to a file named plot«JOB ID».gnuplot.
set terminal png size 640,640 set output "wiki9805558.png" set multiplot layout 2,1 set xrange [0:550] set yrange [0:80] set key on set title "Tasks on 2 nodes by time (seconds)" set key on plot "count.data" u 1:3 t "r00n10.localdomain.hpc.udel.edu" w filledcurves,"count.data" u 1:2 t "r00n47.localdomain.hpc.udel.edu" w filledcurves set title "User time usage rate on all nodes" plot "usage.data" u 1:2 w steps t "CPU"
To create the plot we will need to request an interactive compute node on the devel partition. Once the request has been filled we will need to use VALET to load the gnuplot application and run the plot«JOB ID».gnuplot script that we just created. After the script is ran we will release the node and then view the .png that was created by the script.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array_II]$ salloc --partition=devel salloc: Granted job allocation 9805971 salloc: Waiting for resource configuration salloc: Nodes r00n56 are ready for job [traine@r00n56 MCR_array_II]$ vpkg_require gnuplot Adding package `gnuplot/5.2.4` to your environment [traine@r00n56 MCR_array_II]$ gnuplot plot9805558.gnuplot [traine@r00n56 MCR_array_II]$exit [(it_css:traine)@login00 MCR_array_II]$ display wiki9805558.png
An example of the .png file that is created by the plot9805558.gnuplot script.
Perl Script For Compiled Matlab
WGET DIRECTLY TO THE LOCATION YOU WOULD LIKE IT. YOU COULD ALSO DOWNLOAD IT LOCALLY AND WITH SCP TRANSFER TO BACK TO CAVINESS.
- wikigather.pl
$pattern = '\-(9805558)\-(\d+)\.(out)'; # Make sure to change 9805558 to make your job id. $countFile = 'count.data'; # task count on nodes by seconds $usageFile = 'usage.data'; # accumulate user time on all nodes by seconds $nodeUsageFile = "nodeusage.data"; #detail of node usage by seconds $nodeUsageFiles = "%s_usage.data"; # %s -> host @varNames = qw/sd dim maxe/; # used for columns in resultfile $resultFile = "result%s.data"; # %s -> project id &scandir("."); @node = sort keys %hostCount; foreach $jobid (keys %startTime) { my $file = sprintf "wiki%s.txt", $jobid; open(WIKI, ">$file"); print WIKI `date -d \@$startTime{$jobid} +\"SGE array job started %c\n"`; print WIKI "Used a total of $userTotal{$jobid} CPU seconds "; print WIKI "over ",$stopTime{$jobid}-$startTime{$jobid}," seconds of elapsed time "; print WIKI "on ",0+@node," nodes\n"; $baseTime = $startTime{$jobid} if (!defined $baseTime or $startTime{$jobid} < $baseTime); $avgMaxEig=0; $count=0; if ($resultFile) { my $file = sprintf $resultFile, $jobid; open(DATA, ">$file"); print DATA "@varNames\n"; foreach $task (sort { $a <=> $b } keys %{$result{$jobid}}) { my %var = split($;,$result{$jobid}{$task}); print DATA "@var{@varNames}\n"; $avgMaxEig += $var{'maxe'}; $count += 1; } close(DATA); print 'avgMaxEig = ', $avgMaxEig/$count, "\n"; } printf WIKI "^ %18s ^^ %30s ^^^ %12s ^\n","Node ","Real Clock Time ","Ratio "; printf WIKI "^ %8s ^ %8s ^ %9s ^ %9s ^ %9s ^ %12s ^\n","Name ","Count ","Min ","Max ","Average ","User/Real "; foreach (@node) { if ( $hostCountByJob{$jobid}{$_} > 0) { printf WIKI "|%8s|%8d| %9.2f|%9.2f|%9.2f |%12.5f|\n", $_, $hostCountByJob{$jobid}{$_}, $hostRealMin{$jobid}{$_},$hostRealMax{$jobid}{$_}, $hostReal{$jobid}{$_}/$hostCountByJob{$jobid}{$_}, $hostUser{$jobid}{$_}/$hostReal{$jobid}{$_}; } } close(WIKI); } if ($countFile and open(DATA,">$countFile")) { my(@col,%byNode,$time,$count); $col[$_] = 0 for $[ .. $#node; foreach $time (sort { $a <=> $b } keys %timeCount) { printf DATA "%d %s\n", $time-$baseTime, "@col"; $byNode{$_} += $timeCount{$time}{$_} foreach keys %{$timeCount{$time}}; $count=0; $col[$_] = $count += $byNode{$node[$_]} for $[ .. $#node; printf DATA "%d %s\n", $time-$baseTime, "@col"; } close(DATA); } if ($usageFile and open(DATA,">$usageFile")) { my ($time, $lastTime, $slope, $usage); foreach $time (sort { $a <=> $b } keys %timeRate) { $usage += $slope*($time - $lastTime); $slope += $timeRate{$time}{$_} foreach keys %{$timeRate{$time}}; printf DATA "%d %.4f %.4f\n", $time-$baseTime, $slope, $usage; $lastTime = $time; } close(DATA); } if ($countFile and $usageFile) { foreach $jobid (keys %startTime) { my $plotTitle = 'Number of tasks on %s by time (seconds)'; # %s -> nodes my(@plot); $plot[$_] = "\"$countFile\" u 1:".(2+$_-$[)." t \"$node[$_]\" w filledcurves" for $[ .. $#node; my $plotTop = join(",",reverse @plot); my $titleTop = sprintf $plotTitle, 0+@node." nodes"; my $key = "off"; my ($t1,$t2) = (30*int(($startTime{$jobid}-$baseTime)/30),30*int(2+($stopTime{$jobid}-$baseTime)/30)); $titleTop = sprintf $plotTitle, "nodes @node" if $#node < 5; $key = "out horiz top right" if $#node < 9; open (PLOT, "| gnuplot" ); print PLOT <<"EOP"; set term pngcairo font "sans,10" size 640,640 set output "wiki$jobid.png" set multiplot layout 2,1 set xrange [$t1:$t2] set key $key set ylabel "Number of Tasks on node" plot $plotTop set key out horiz top right set ylabel "Total CPU usage" set xlabel "Time (seconds)" plot "$usageFile" u 1:3 w lines t "CPU seconds" EOP } } sub scanfile { my($file) = @_; my($jobid,$taskid) = ($file =~ /$pattern/); my($host,$start,$finish,$usr1,$usr2,$real,$user,$sys,$lhs,%var); open(FILE,$file) || next; local $/ = undef; #Read file as one string while (<FILE>) { study; /^Host (\S+)/m and $host=$1; /^Start (\d+)/m and $start=$1; /^Finish (\d+)/m and $finish=$1; /^SIGUSR1 (\d+)/m and $usr1=$1; /^SIGUSR2 (\d+)/m and $usr2=$1; /^real(.*?)m(.*?)s/m and $real=60*$1+$2; /^user(.*?)m(.*?)s/m and $user=60*$1+$2; /^sys(.*?)m(.*?)s/m and $sys=60*$1+$2; while(/(\S+)\s*=\s*(.*)/g) { $var{$1}=$2 }; } close(FILE); $result{$jobid}{$taskid} = join($;,%var); $SGEfile{$file} = sprintf "| %s | %.2f %8.2f %8.2f |", $host, $real, $user, $sys; $SGEfile{$file} .= sprintf " %d %d |", $usr1, $usr2; $SGEfile{$file} .= join(',', map {" $_=$var{$_}"} keys %var ); $finish = $usr2 if( $finish==0 ); $finish = $usr1 if( $finish==0 ); $finish > 0 || next; $real = $finish-$start if($real==0); $user = $real-$sys if($user==0); $startTime{$jobid} = $start if (!defined $startTime{$jobid} or $start < $startTime{$jobid}); $stopTime{$jobid} = $finish if (!defined $stopTime{$jobid} or $finish > $stopTime{$jobid}); $userTotal{$jobid} += $user; $hostCount{$host} += 1; $hostCountByJob{$jobid}{$host} += 1; $hostReal{$jobid}{$host} += $real; $hostRealMax{$jobid}{$host} = $real if (!defined $hostRealMax{$jobid}{$host} or $real > $hostRealMax{$jobid}{$host}); $hostRealMin{$jobid}{$host} = $real if (!defined $hostRealMin{$jobid}{$host} or $real < $hostRealMin{$jobid}{$host}); $hostUser{$jobid}{$host} += $user; $timeCount{$start}{$host} += 1; $timeCount{$finish}{$host} -= 1; $timeRate{$start}{$host} += $user/($finish-$start); $timeRate{$finish}{$host} -= $user/($finish-$start); } sub scandir { my($basedir) = @_; my(@file,@dir); opendir(DIR, $basedir) || return; foreach ( grep (/^[^\.]/,readdir(DIR)) ) { # ignore hidden files next if -l "$basedir/$_" ; # skip sym links push @file,$_ if /$pattern/; # save files with this pattern push @dir,$_ if -d "$basedir/$_" ; # save directories for recursion } closedir(DIR); foreach (@file) { &scanfile("$basedir/$_"); } foreach (@dir) { &scandir("$basedir/$_"); } }
Adding checkpoints Matlab job example
Adding checkpoints to your Matlab job could help it to gracefully handle kill signals from the system. The proper handling of these signals can help you restart your job without having to start completely over again. In the following example, we will modify previously used scripts and functions to track which interval the loop stops at when the job times out.
Gathering code for job example
First, we'll create a new directory and copy the needed code into it.
[(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_example [(it_css:traine)@login00 matlab_example]$ mkdir matlab_checkpoint [(it_css:traine)@login00 ~]$ cd matlab_checkpoint [(it_css:traine)@login00 matl_checkpoint]$ cp /opt/shared/templates/slurm/generic/serial.qs batch.qs
You will also want to put a copy of the maxEig.m and script.m into your matlab_checkpoint directory.
Now we will need to make changes to script.m. The added code block reads the count and records it as the checkpoint for the loop interval, and it will restart from the checkpoint instead from the beginning once the job fails.
% script to run maxEig function 200 times and print average.
count = 200;
dim = 5001;
sumMaxe = 0;
i = 0;
id = str2num(getenv('SLURM_JOB_ID'));
rc = 0;
rc = str2num(getenv('SLURM_RESTART_COUNT'));
tic;
if isempty(rc);
for i=1:count;
sumMaxe = sumMaxe + maxEig(i,dim);
counter = "counter: "+i; %Add this line
disp(counter); %Add this line
end;
else
filename = ['checkpoint-', num2str(id), '.out']; % Specify the file name where you want to search
searchString = 'ended on counter'; % Specify the string you want to search for
fileID = fopen(filename, 'r'); % Open the text file for reading
if fileID == -1
error('Unable to open the file.');
end
lineNumber = 0;
% Read lines from the file and search for the target string
while ~feof(fileID)
line = fgetl(fileID);
if ischar(line)
lineNumber = lineNumber + 1;
if ~isempty(strfind(line, searchString))
num=regexp(line,'counter:\s(\d+)', 'tokens');
counterNumber = str2double(num{1}{1});% Record the counter number
end
end
end
fclose(fileID); % Close the file
for i =counterNumber:count; % Once the job restarted, it will continue from the last counter number
sumMaxe = sumMaxe + maxEig(i,dim);
counter = "counter: "+i;
disp(counter);
end;
end;
toc
avgMaxEig = sumMaxe/count
quit
The following changes will need to be added to batch.qs. The option –requeue allows job to restart, and scontrol requeue will automatically restart the job once it fails.
...
40 #SBATCH --job-name=checkpoint
...
60 #SBATCH --time=0-01:30:00
...
75 #SBATCH --output=%x-%j.out
76 #SBATCH --error=%x-%j.out
...
85 #SBATCH --mail-user='traine@udel.edu'
86 #SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL,TIME_LIMIT_90
87 #SBATCH --requeue # allow job requeue
88 #SBATCH --open-mode=append # the output will append
...
90 max_restarts=1 #only requires a single restart
91 scontext=$(scontrol show job $SLURM_JOB_ID)
92 restarts=$(echo "$scontext" | grep -o 'Restarts=.' | cut -d= -f2) # get the restart number
93 job_exit_handler() {
94 counter=$(tail -n 2 ${SLURM_JOB_NAME}-${SLURM_JOB_ID}.out | head -n 1)
95 echo "Job ${SLURM_JOB_NAME} ended on ${counter}"
96 if [[ $restarts -lt $max_restarts ]];then
97 scontrol requeue ${SLURM_JOB_ID} #automatically resubmit the job once
98 #matlab -nodisplay -nojvm -batch disp(getReport(err,'extended')); quit;"
99 # Copy all our output files back to the original job directory:
100 #cp * "$SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR"
101
102 # Don't call again on EXIT signal, please:
103 trap - EXIT
104 exit 0
105 else
106 trap - EXIT
107 echo "Your job is over the Maximum restarts limit"
108 exit 1
109 fi
110 }
111
112 export UD_JOB_EXIT_FN=job_exit_handler
...
142 #
143 #srun date
144 export UD_JOB_EXIT_FN_SIGNALS="SIGTERM EXIT"
145 #Loading MATLAB
146 vpkg_require matlab/r2019b
147 #Running the matlab script
148 UD_EXEC matlab -nodisplay -nojvm -batch "try; script; catch ERR; disp(job_exit_handler(ERR.getReport)); quit; end"
Running the checkpoint job and its output
We know from the MCR example that this script takes between 2-3 hours to run. In the changes we made to batch.qs script, we set the wall clock to 40 minutes to demonstrate the usage of the script. That should ensure that this script will fail to complete before the wall clock runs out of time. This is shown in the following job submission example.
[(it_css:traine)@login01 matlab_checkpoint]$ sbatch batch.qs Submitted batch job 20426672
After the wall clock runs out we will see the following output.
[(it_css:traine)@login01 matlab_checkpoint]$ less checkpoint-20426672.out Adding package `matlab/r2019b` to your environment -- Registered exit function 'job_exit_handler' for signal(s) SIGTERM EXIT maxe = 70.0220 counter: 1 maxe = 71.7546 counter: 2 maxe = 70.8331 counter: 3 maxe = 70.5714 counter: 4 maxe = 69.4923 counter: 5 ... maxe = 70.2614 counter: 53 slurmstepd: error: *** JOB 20426672 ON r01n13 CANCELLED AT 2023-10-03T17:31:54 DUE TO TIME LIMIT *** Job 20426672 ended on counter: 53 Adding package `matlab/r2019b` to your environment -- Registered exit function 'job_exit_handler' for signal(s) SIGTERM EXIT maxe = 70.2614 counter: 53 maxe = 58.9360 counter: 54 maxe = 69.0119 counter: 55 ... maxe = 70.7254 counter: 104 maxe = 65.5558 counter: 105 slurmstepd: error: *** JOB 20426672 ON r01n13 CANCELLED AT 2023-10-03T18:19:25 DUE TO TIME LIMIT *** Job 20426672 ended on counter: 105 Your job is over the Maximum restarts limit
Now we know that the script completed about 53 of the 200 loop intervals before the wall clock expired. Then it restarts from the 53 loop interval and finally stops at 105 due to reaching the maximum restart limit we set up.
[(it_css:triane)@login01 matlab_checkpoint]$ sbatch batch.qs
Submitted batch job 8390581
[(it_css:traine)@login01 matlab_checkpoint]$ scancel 8390581
[(it_css:traine)@login01 matlab_checkpoint]$ cat checkpoint-8390581.out
-- Registered exit function 'job_exit_handler' for signal(s) SIGTERM
Adding package `matlab/r2019b` to your environment
maxe =
70.0220
counter: 1
...
maxe =
67.7814
counter: 6
maxe =
70.5037
counter: 7
slurmstepd: error: *** JOB 8390581 ON r00n17 CANCELLED AT 2020-05-21T10:55:03 ***
Job checkpoint ended on counter: 7